The Benefits of Turmeric…
wait… what is Turmeric anyway?
In the U.S., turmeric is best known as a spice. It’s one of the main components of curry powder. In India and other parts of Asia, turmeric is used to treat many health conditions. It is believed to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and perhaps even anti-cancer properties.

Why do people take Turmeric as a supplement?
Turmeric contains compounds called curcuminoids, the most important of which is curcumin.
Curcumin is the main active ingredient in turmeric. It has powerful anti-inflammatory effects and is a very strong antioxidant. However, the curcumin content of turmeric itself is not that high, as it’s only around 3%, by weight, so having it in a soup or curry once in a while is not likely to give you the desired anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits you’re hoping for. [1] To consume the amounts of turmeric and curcumin levels shown to offer benefits in the research studies, you’ll want to turn to supplements.
Unfortunately, turmeric (and curcumin on its own) doesn’t absorb well into the bloodstream, although it is fat soluble, so it may be a good idea to take it with a fatty meal. Taking it with coconut oil is a great option as well.
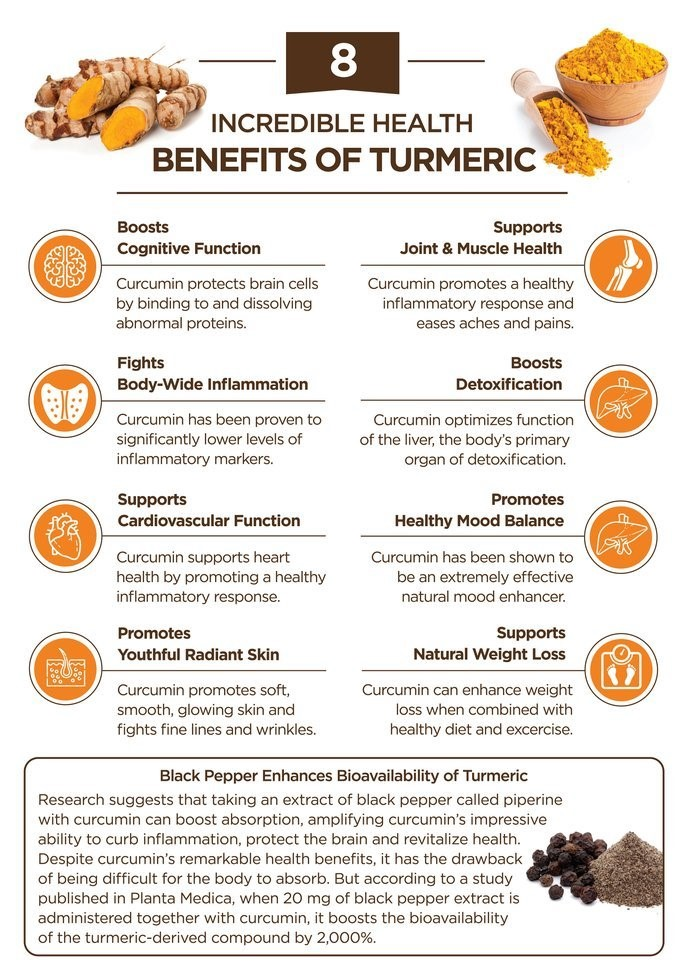
Alternatively, you can reap amazing benefits by adding black pepper anytime you use turmeric (1/20 of a teaspoon will do the trick) [2], or by taking a additional supplement called BioPerine along with your turmeric or curcumin supplement.

The reason that black pepper helps, is a compound called piperine that it contains. Piperine actually helps make turmeric more bioavailable, increasing it’s bioavailability by up to 2,000 percent! (Bioavailability refers to the amount of a substance that’s absorbed or able to be used by the body.) [3]
So What Exactly Does Curcumin Do?
Some studies show that curcumin may help to reduce inflammation. Several other studies suggest that it might ease symptoms of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, like pain and inflammation. [4]
Preliminary lab studies suggest that curcumin or turmeric might protect against types of colitis, stomach ulcers, and high cholesterol. Based on additional studies, turmeric and curcumin might also help treat upset stomach, diabetes, depression, HIV, uveitis, and viral infections. [4]
In lab tests, curcumin appears to block the growth of certain kinds of tumors. One study showed that turmeric extract containing curcumin could — in some cases — stabilize colorectal cancer that wasn’t helped by other treatments. [4]
Initial studies have even found that turmeric’s curcumin can protect against oxidative damage and sleep deprivation. Slip this super spice into your bedtime ritual to relax, improve mood, help depression , and potentially lower your anxiety levels. [5]
Try this awesome Golden Milk Latte as part of your bedtime ritual.
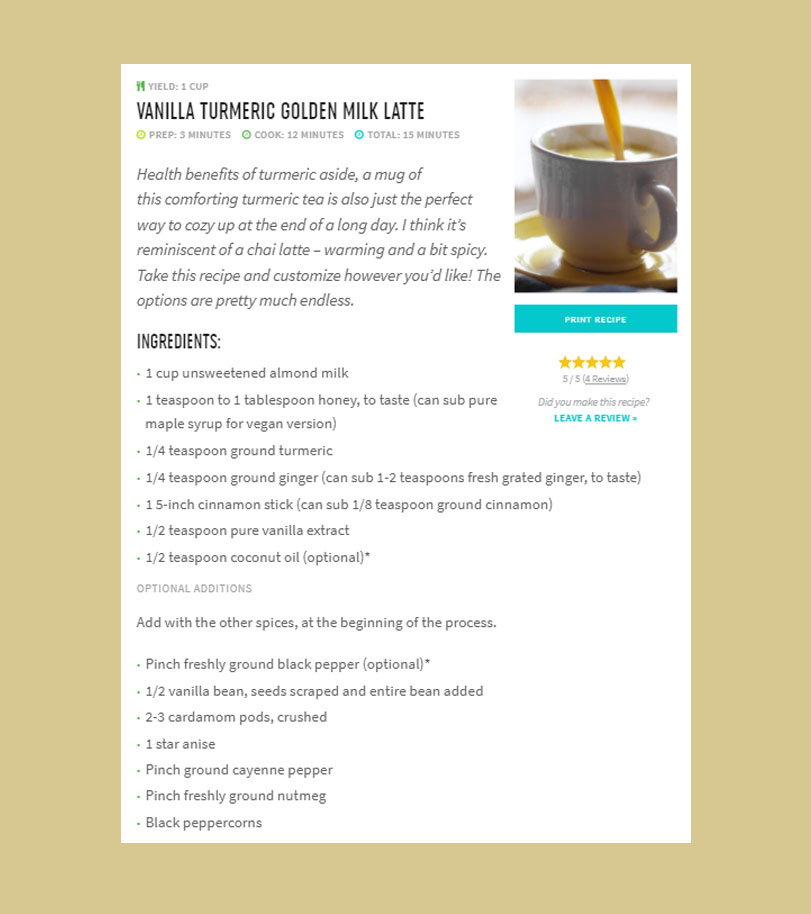
There’s no shortage of internet articles about the benefits of turmeric, and the health claims about curcumin. And it’s no surprise that the supplements are gaining momentum. But what does the actual research say?
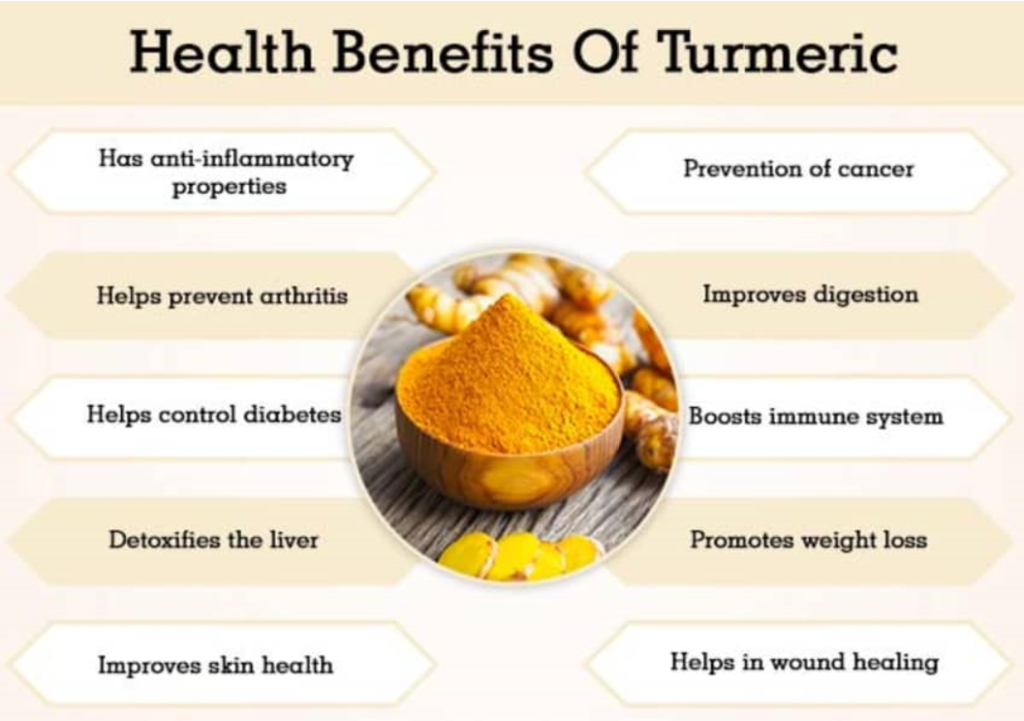
Here are some of the many potential benefits of turmeric and curcumin, and the studies that back them up.
1. Curcumin is an Effective Anti-Inflammatory
Scientists now believe that chronic, low-level inflammation plays a major role in almost every chronic, Western disease. This includes cancer, heart disease, metabolic syndrome, Alzheimer’s and other various degenerative conditions [6].
As a result, anything that can help fight chronic inflammation is of significant importance in preventing and even treating these diseases.
Curcumin is strongly anti-inflammatory. In fact, it’s so powerful that it matches the effectiveness of some anti-inflammatory drugs, without the side effects. [6]
2. Curcumin Protects Your Body From Free Radicals and Increases the Antioxidant Capacity of the Body
Curcumin is a potent antioxidant that can neutralize free radicals due to its chemical structure.
In addition, curcumin boosts the activity of your body’s own antioxidant enzymes.
Antioxidants help protect your body against damage caused by free radicals, a class of highly reactive atoms that are generated in our bodies, as well as in environmental pollutants like cigarette smoke and industrial chemicals. (34) Too much exposure to free radicals can mess with the fats, proteins, and even DNA in your body, which may lead to a number of common diseases and health conditions, including cancer, arthritis, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s. (34)
Curcumin in particular is able to scavenge different types of free radicals, control enzymes that neutralize free radicals, and prevent certain enzymes from creating specific free radical types, according to a review in the October 2017 issue of Foods. (35) [6]
In this way, curcumin delivers a one-two punch against free radicals. It blocks them directly, then stimulates your body’s own antioxidant defenses.
3. Curcumin May Protect Against Heart Disease
Perhaps the main benefit of curcumin when it comes to heart disease is improving the function of the endothelium, which is the lining of your blood vessels.
It’s well known that endothelial dysfunction is a major driver of heart disease and involves an inability of your endothelium to regulate blood pressure, blood clotting and various other factors (29Trusted Source).
“A past study shows that curcumin may improve endothelial function, which is the health of the thin membrane that covers the inside of the heart and blood vessels. This membrane plays a key role in regulating blood pressure. (6) Lower endothelial function is associated with aging and an increased risk of heart disease. Thus, curcumin may help protect against age-related loss of function and reduce your likelihood of developing heart disease.
In one study, researchers compared the effects of an eight-week aerobic exercise program and a curcumin supplement in improving endothelial function in postmenopausal women. Both the exercise and the curcumin group saw equal improvements in endothelial function, whereas the control group saw no changes. (7)
Another study found that curcumin was equally effective at improving endothelial function in people with type 2 diabetes (heart disease is a common comorbidity of type 2) as the drug Lipitor (atorvastatin), a medication commonly prescribed to reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke. (8,9,10) [6]
4. Curcumin May Prevent (and Possibly Help Treat) Cancer
It is possible that curcumin will be used along with conventional cancer treatment one day. It’s too early to say for sure, but it looks promising and is being intensively studied. Some of the studies are listed below.
Curcumin has been studied as a beneficial herb in cancer treatment and been found to affect cancer growth, development and spread at the molecular level. [7]
Studies have shown that it can contribute to the death of cancerous cells and reduce angiogenesis (growth of new blood vessels in tumors) and metastasis (spread of cancer). [8]
Multiple studies indicate that curcumin can reduce the growth of cancerous cells in the laboratory and inhibit the growth of tumors in test animals. [9] [10]
Whether high-dose curcumin (preferably with an absorption enhancer like piperine) can help treat cancer in humans has yet to be studied properly.
However, there is evidence that it may prevent cancer from occurring in the first place, especially cancers of the digestive system like colorectal cancer.
In a 30-day study in 44 men with lesions in the colon that sometimes turn cancerous, 4 grams of curcumin per day reduced the number of lesions by 40%. [11]
As inflammation is linked to tumor growth, anti-inflammatory compounds such as curcumin may play a role in treating and preventing a variety of cancer types, including colorectal, pancreatic, prostate, breast, and gastric cancers. (1) In fact, research in mice suggests that curcumin may help slow the spread of tumor cells and may even prevent tumors from forming in the first place. (11) It may do this in several ways, including disrupting the formation of cancerous cells at various stages in the cell cycle, interfering with cell signaling pathways, and even causing those cancerous cells to die. (11) [6]
5. Curcumin May Help Ease Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
Thanks to its potent anti-inflammatory properties, curcumin may be a safe and effective long-term treatment option for people with osteoarthritis (OA).
In a past study, people with osteoarthritis who took 1,000 mg/day of Meriva experienced significant improvements in stiffness and physical function after eight months, whereas the control group saw no improvements. Meriva is a proprietary treatment made up of a natural curcuminoid mixture (75 percent curcumin; 15 percent demethoxycurcumin; and 10 percent bisdemethoxycurcumin), phosphatidylcholine (a chemical found in eggs, soybeans, and other foods), and microcrystalline cellulose (a refined wood pulp commonly used by the pharmaceutical and food industries). (12,13,14) [6]
And a study in mice published in the June 2016 issue of Arthritis Research & Therapy found that 50 mg oral curcumin per kilogram (kg) body weight significantly slowed the progression of OA, whereas a topical curcumin treatment provided pain relief. [6]
6. Curcumin May Help Treat or Prevent Diabetes
According to a review of previous studies, curcumin may help treat and prevent diabetes, as well as associated disorders like diabetic nephropathy (also called diabetic kidney disease), which affects people with type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Unfortunately many of the studies are still awaiting human trials.
One study found that feeding 80 mg of tetrahydrocurcumin (one of the main substances of curcumin) per kg body weight to rats with type 2 diabetes for 45 days led to a significant decrease in blood sugar, as well as an increase in plasma insulin. (18) [6]
A study in obese mice with type 2 diabetes published in the July 2019 issue of Nutrition & Metabolism reveals that curcumin supplements helped lower blood insulin levels after 16 weeks. (19) [6]
Curcumin may help prevent diabetes through its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, and improve many of the factors that contribute to diabetes, including insulin resistance, high blood sugar, and hyperlipidemia (a medical term to describe elevated levels of fat in the blood; one type of hyperlipidemia is characterized by high levels of LDL, or “bad,” cholesterol). (20,16) [6]
7. Curcumin Boosts Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Linked to Improved Brain Function and a Lower Risk of Brain Diseases
We know that the neurons in our brain are capable of forming new connections, and in certain areas of the brain they can also multiply and increase in number. One of the main drivers of this process is brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is a type of growth hormone that functions in your brain. [12] BDNF is a protein found in the brain and spinal cord that plays a key role in keeping nerve cells (neurons) healthy, as well as regulating communication between nerve cells, which is critical for learning and memory.
Many common brain disorders have been linked to decreased levels of this BDNF hormone, including depression and Alzheimer’s disease. [13] [14]
Interestingly, curcumin can increase brain levels of BDNF, and by doing this, it may be effective in delaying or even reversing many brain diseases and age-related decreases in brain function. [15]
It may also improve memory and make you smarter, which seems logical given its effects on BDNF levels. [16]
8. Curcumin May Help Prevent, Delay, Treat, and even Reverse Alzheimer’s Disease
It’s known that inflammation and oxidative damage play a role in Alzheimer’s disease, and as we’ve already discussed, curcumin has beneficial effects on both thru its effects on the BDNF hormone. (see above for more detailed BDNF description). Here are some key studies and their finding concerning Alzheimer’s Disease.
Curcumin has been shown to cross the blood-brain barrier and has been shown to lead to various improvements in the pathological process of Alzheimer’s disease. [17]
As common brain disorders like Alzheimer’s are associated with lower levels of BDNF, turmeric (curcumin in particular) may help delay or reverse brain degeneration. (22,23,24) [6]
In addition, a key feature of Alzheimer’s disease is a buildup of protein tangles called amyloid plaques. Studies show that curcumin can help clear these plaques. [18]
9. Curcumin May Help Treat Depression
Like Alzheimer’s, depression is also associated with lower levels of BDNF. Thanks to curcumin’s ability to boost levels of BDNF, it shows promise as an effective antidepressant.
In a study in humans that was published in the April 2014 issue of Phytotherapy Research, researchers randomly assigned 60 patients with major depressive disorder to one of three groups: one group received daily 20 mg of fluoxetine (Prozac is a common brand name), another received 1,000 mg of curcumin, and a third received a combination of the two. By the end of six weeks, the three groups saw comparable improvements, leading researchers to suggest that curcumin may be a safe and effective treatment for major depressive disorder. (26,27)[6]
In addition, there is also some evidence that curcumin can boost the brain neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine. [19]
10. Curcumin May Play a Vital Role in Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis
Arthritis is a common chronic inflammatory disorder that generally affects the joints but may spread to other areas, such as the eyes, lungs, skin, heart, and blood vessels. RA causes a painful swelling of the joints that can cause the bones to erode over time and ultimately lead to deformities and physical disabilities. Numerous studies show that curcumin can help treat symptoms of arthritis and is in some cases more effective than anti-inflammatory drugs.
In one study, people with RA were given 500 mg of curcumin, 50 mg of diclofenac sodium (a prescription nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug), or the two in combination. (30) After eight weeks, the curcumin-only group saw significant improvements in joint tenderness and swelling when compared with the other two groups. Researchers note the curcumin treatment was also safe, resulting in no harmful events. (31) [6]
11. Curcumin May Improve Skin Health
Thanks to its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties, turmeric may be an effective treatment for a variety of skin conditions, including acne, eczema (atopic dermatitis), photoaging, and psoriasis.
One review published in the January 2018 issue of Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences suggests oral curcumin in particular may be an effective and safe treatment option for psoriasis (a chronic inflammatory skin disease), but more studies are needed before making recommendations. (32) [6]
According to the authors of another review, topical curcumin treatments may be useful in treating skin disorders, especially as past research suggests curcumin is relatively safe even at high doses. [6]
12. Curcumin May Help Prevent Eye Degeneration
Glaucoma, a group of eye conditions, is one of the leading causes of blindness in people over age 60. And, unfortunately, once your vision is gone, there’s not much that can be done to restore it. Therefore finding ways to prevent glaucoma are crucial for maintaining your vision as your body ages.
Preliminary research published July 2018 in Scientific Reports shows topical curcumin treatments may help protect the eyes against degeneration.
Researchers applied a proprietary curcumin eye drop solution to rats two times per day for three weeks. By the end of the study, the untreated rats experienced a 23 percent reduction in retinal cells compared with the treatment group, suggesting that loss was prevented by the curcumin treatment. (38) [6]
13. Curcumin May Help Delay Aging and Fight Age-Related Chronic Diseases
Given that oxidation and inflammation are believed to play a role in aging, curcumin may have effects that go way beyond just preventing disease. Thanks to their ability to fight inflammation, protect your body against free radicals, and potentially delay brain degeneration and other age-related diseases, turmeric and curcumin are quickly becoming very popular as anti-aging supplements. [6]
The Benefits of Turmeric Supplements: Getting Started
As you can see – we are just starting to understand the full spectrum of uses and benefits of turmeric and curcumin. It is no surprise that turmeric and curcumin supplements are gaining wide-spread momentum.
One of the main things you’ll want to look for in a turmeric / curcumin supplement is that it is made from the highest quality ingredients.

The Ukon® supplements are among the highest-quality turmeric supplements on the market. They are made with all organically grown Wild Turmeric (also known as Spring Ukon), that is directly sourced.
To learn more about this incredibly high-grade turmeric supplement, please use the chat function on this website to send me a message or contact me.
Resources:
[1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17044766
[2] https://www.umassmed.edu/nutrition/blog/blog-posts/2019/6/using-black-pepper-to-enhance-the-anti-inflammatory-effects-of-turmeric/
[3] https://www.everydayhealth.com/diet-nutrition/diet/scientific-health-benefits-turmeric-curcumin/
[4] https://www.webmd.com/diet/supplement-guide-turmeric#1
[5] https://www.healthline.com/health/food-nutrition/warm-milk-to-sleep
[6 ] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/top-10-evidence-based-health-benefits-of-turmeric#section2
[7 ] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18462866
[8 ] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2758121/
[9] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9973206
[10] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20214562
[11] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21372035
[12] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2504526/
[13] https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0006322303001811
[14] https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0896627391902733
[15] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3281036/
[16] https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10522-013-9422-y
[17] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2781139/
[18] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16988474
[19] https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00213-008-1300-y




